Ohm's Law Calculator
How to Use the Ohm's Law Calculator
This Ohm's Law Calculator allows you to find any two unknown values—Voltage (V), Current (I), Resistance (R), or Power (P)—when you know any other two. Simply enter the two known values and leave the other fields blank to calculate the remaining two values.
- Step 1: Enter the two values you know in their respective fields.
- Step 2: Leave the fields for the unknown values blank.
- Step 3: Click the "Calculate Missing Values" button to compute the remaining values.
This calculator applies Ohm's Law and power formulas to solve for the missing values, providing a clear breakdown of each calculation step.
Understanding Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering and physics, defining the relationship between Voltage (V), Current (I), and Resistance (R). Using this law, we can derive various formulas for calculating power (P) as well, making it essential for analyzing electrical circuits.
1. The Ohm's Law Formula Wheel
The Ohm's Law Formula Wheel is a quick reference tool that shows all possible combinations of these formulas to calculate Voltage, Current, Resistance, and Power. Here is a breakdown:
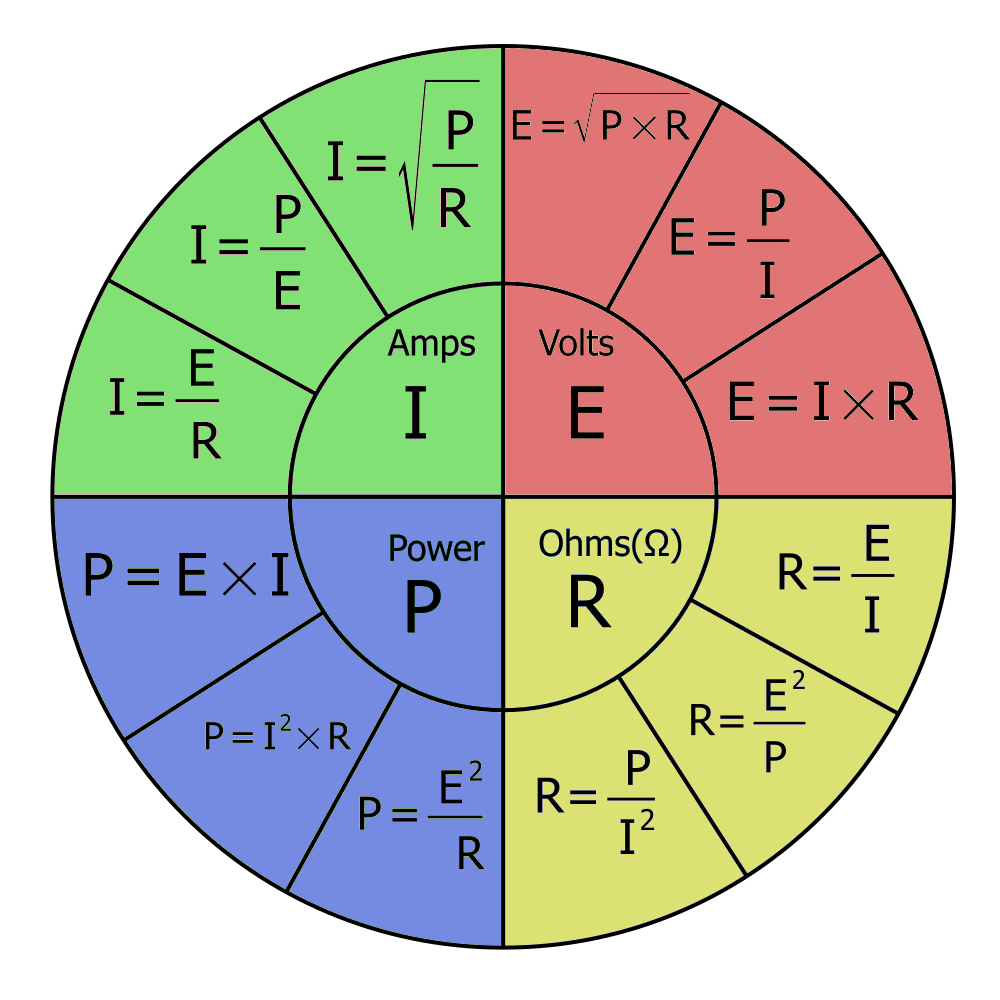
In the Ohm's Law Formula Wheel, you’ll see the formulas arranged to quickly find any missing value based on the other known values. Here’s how they’re derived:
- Voltage (V) = Current (I) * Resistance (R)
- Current (I) = Voltage (V) / Resistance (R)
- Resistance (R) = Voltage (V) / Current (I)
- Power (P) = Voltage (V) * Current (I)
- Power (P) = Current² (I²) * Resistance (R)
- Power (P) = Voltage² (V²) / Resistance (R)
2. Practical Applications of Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law is crucial for designing and troubleshooting electrical circuits. It allows us to calculate the required resistance for a circuit, determine the power consumed, and ensure that components are not overloaded. It is widely used in various fields, from simple electronic devices to complex electrical engineering projects.
3. Tips for Using Ohm's Law in Calculations
Remember to keep units consistent when performing calculations. For example, if you use volts for voltage, amperes for current, and ohms for resistance, the resulting power will be in watts. Converting units correctly is essential, especially when working with large or small values.
This Ohm's Law Calculator and Formula Wheel make it easy to find missing values and understand the interrelationships between voltage, current, resistance, and power.
Explore Our Calculators
Math Calculators
Finance Calculators
Health Calculators
Science & Engineering Calculators
Explore Programming Tools
Programming Tools
Explore our interactive programming environments for learning, testing, and executing code directly in your browser. Perfect for students, professionals, and enthusiasts.